微服务 断路器
业务问题场景
在业务系统中,通常存在服务之间的相互调用,例如服务A调用服务B,当出现如下情形:
- 服务A与服务B之间的网络出现异常
- 服务B过载
- 服务B出现异常
服务A应该减少对服务B的调用量,甚至服务A应该停止调用服务B,有必要的话,还可以采取相应的降级措施`。当服务B恢复正常后,才开始继续调用服务B。
断路器模式
在家庭电路中有一个叫断路器的安全设备,当出现电路过载、短路、漏电等情况时,就会发生跳闸,防止出现安全事故。类比到上面描述的业务问题场景,我们需要在系统中实现一个类似断路器功能的组件,用于阻止系统A重复尝试很可能失败的调用。
在断路器模式中,断路器组件需要监测到最近失败的调用,并且利用这些信息去决定新的调用是否执行,还是立即抛出异常。当断路器组件“跳闸”之后,还需要能探测被调用服务是否恢复正常,
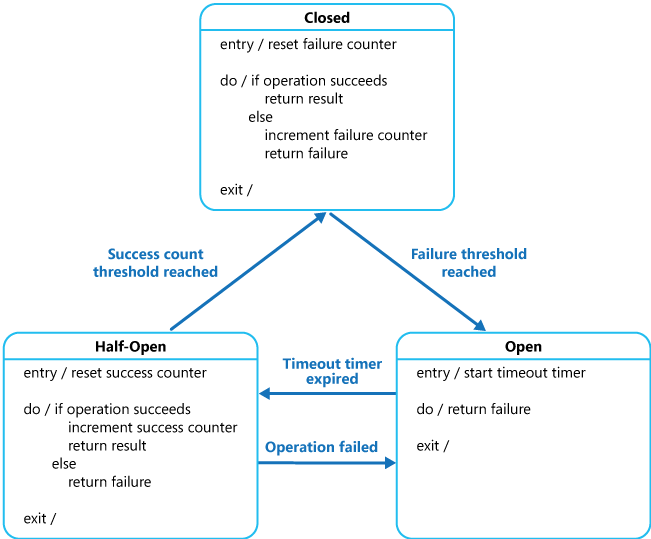
断路器模式的代码实现,使用了有限状态机的思想。最基本的实现有三种状态:
- 关闭(Closed):调用正常执行。断路器组件对最近失败的调用进行计数,当达到阈值时,则断路器组件“跳闸”,进入“打开”状态。
- 打开(Open):调用请求会立即失败,断路器组件抛出异常。
- 半打开(Half-Open):当处于“打开”状态时,会启动一个超时定时器,当超时后,断路器组件会进入“半打开”状态,此时允许执行部分调用,断路器会对成功执行的调用进行计数,达到阈值后,会认为被调用服务恢复正常,断路器状态回到“关闭”状态,如果有请求出现失败,则回到“打开”状态。
问题和注意事项
- 异常处理:系统需要考虑到断路器抛出的各类异常该如何处理。比如采取降级措施,把请求转发给备份服务,或者通知上游稍后重试。
- 异常的类型:服务调用请求可能出现超时,或网络不通,下游服务明确返回失败的情况,断路器可能需要针对不同情况的错误,采取不同的状态切换策略。例如触发切换到“打开”状态的条件,可以是超时错误的阈值比下游服务明确返回失败的阈值更高。
- 日志:断路器需要记录下所有失败的请求,方便相关人员监控定位问题。
- 恢复:配置合适的策略,让断路器检测下游服务是否恢复正常,
- “打开”到“半打开”的状态切换:可以不使用定时器,而是周期性的探测下游服务是否恢复。
- 人为干预:服务异常恢复需要的时间有长有短,断路器最好能提供人为控制的接口,方便将断路器强制切换到“打开”或“关闭”状态。
- 并发:一个断路器可能会被很多请求并发访问,所以断路器工程化实现所需的时间和空间消耗需要尽量的小。
- 资源差异:为不同的资源访问,单独创建相应的断路器。
- 加速“跳闸”:当可以从下游服务获取到足够明确的异常时,则立即切换到“打开”状态。
Golang中断路器的实现:cep21/circuit
github.com/cep21/circuit 实现了类似 Hystrix(Java版本)的断路器模式。在示例代码circuit/v3/example/main.go中,模拟了服务调用可能出现的各种情况,以及对应的断路器配置,以下我总结了对该库的理解和应用。
cep21/circuit中主要的类型和接口:
circuit.Manager
// 管理多个circuits对象实例
type Manager struct {
// func (h \*Manager) CreateCircuit(name string, configs ...Config) (\*Circuit, error) 方法创建circuits对象实例时,使用的配置,会按照逆序将多个配置合并为最终的配置
DefaultCircuitProperties []CommandPropertiesConstructor
// 每个circuits会有一个唯一命名的标识
circuitMap map[string]\*Circuit
// 用于circuitMap的读写锁
mu sync.RWMutex
}
circuit.Circuit
type Circuit struct {
//circuitStats
CmdMetricCollector RunMetricsCollection // 统计调用出现的各种情况
FallbackMetricCollector FallbackMetricsCollection // 统计降级调用出现的各种情况
CircuitMetricsCollector MetricsCollection // 统计Circuit状态切换的情况
// This is used to help run `Go` calls in the background
goroutineWrapper goroutineWrapper // 用于异步调用的封装
name string // 断路器唯一命名的标识
notThreadSafeConfig Config // 非线程安全的断路器配置
notThreadSafeConfigMu sync.Mutex
threadSafeConfig atomicCircuitConfig // 线程安全的断路器配置
// Tracks if the circuit has been shut open or closed
isOpen faststats.AtomicBoolean // 断路器只有“打开”和“关闭”两种状态
// Tracks how many commands are currently running
concurrentCommands faststats.AtomicInt64 // 统计有多少并发调用
// Tracks how many fallbacks are currently running
concurrentFallbacks faststats.AtomicInt64 // 统计有多少降级的并发调用
// ClosedToOpen controls when to open a closed circuit
ClosedToOpen ClosedToOpen // 控制断路器由“关闭”状态切换到“打开”状态
// openToClosed controls when to close an open circuit
OpenToClose OpenToClosed // 控制断路器由“打开”状态切换到“关闭”状态
timeNow func() time.Time // 对time.Now的封装,值始终为config.General.TimeKeeper.Now,从config.TimeKeeper的解释看是为了方便测试,当没在测试代码里有看到使用
}
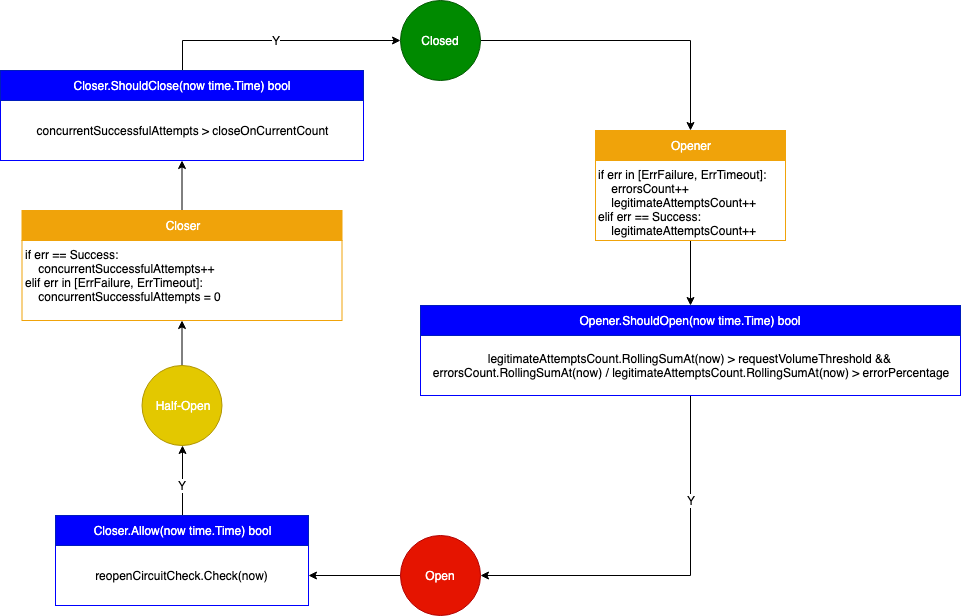
circuit.ClosedToOpen
type ClosedToOpen interface {
RunMetrics // 统计调用出现的各种情况
Metrics // 统计状态切换的情况
// 当出现ErrFailure和ErrTimeout的失败调用时,会调用ShouldOpen,ShouldOpen会根据RunMetrics信息决定是否切换到“打开”状态
ShouldOpen(now time.Time) bool
// 即使断路器处于“关闭”状态,也希望能阻止调用
Prevent(now time.Time) bool
}
circuit/v3/closers/hystrix/opener.go 是 hystrix 的默认实现,实现了 circuit.ClosedToOpen 接口。
type Opener struct {
errorsCount faststats.RollingCounter // 统计调用出现的ErrFailure和ErrTimeout的情况
legitimateAttemptsCount faststats.RollingCounter // 统计调用出现的ErrFailure和ErrTimeout,以及Success的情况
errorPercentage faststats.AtomicInt64 // 错误阈值
requestVolumeThreshold faststats.AtomicInt64 // 如果在一段时间窗口内的调用次数小于该阈值,则不会将断路器切换到“打开”状态
mu sync.Mutex // 修改config时的互斥锁
config ConfigureOpener
}
// faststats.RollingCounter 是滑动窗口计数器,用于统计一段时间窗口内,对每个时间片上发生的事件进行计数
circuit.OpenToClosed
type OpenToClosed interface {
RunMetrics // 统计调用出现的各种情况
Metrics // 统计状态切换的情况
// 当调用成功时,会调用ShouldClose,ShouldClose会根据RunMetrics信息决定是否切换到“关闭”状态
ShouldClose(now time.Time) bool
// “半打开”状态的实现,用于在断路器处于“打开”状态时,允许部分调用执行
Allow(now time.Time) bool
}
circuit/v3/closers/hystrix/closer.go 是 hystrix 的默认实现,实现了 circuit.OpenToClosed 接口。
type Closer struct {
// 当断路器处于“打开”状态时,定时放行部分调用,被OpenToClosed.Allow调用
reopenCircuitCheck faststats.TimedCheck
concurrentSuccessfulAttempts faststats.AtomicInt64 // 当调用为Success时,加1,当调用为ErrFailure、ErrTimeout时,重置为0
closeOnCurrentCount faststats.AtomicInt64 // 切换到“关闭”状态的阈值,在OpenToClosed.ShouldClose中使用
mu sync.Mutex // 修改config时的互斥锁
config ConfigureCloser
}
cep21/circuit 实现的断路器模式有限状态机图解
异常处理
func (c *Circuit) Execute(ctx context.Context, runFunc func(context.Context) error, fallbackFunc func(context.Context, error) error) error 方法返回的 error 可能的情况有:
- runFunc 返回的 error,包括 circuit.BadRequest
- circuit 返回的
- 当状态为“打开”:
circuit.circuitError{concurrencyLimitReached: true, msg: "circuit is open"} - 当并发请求超过阈值:
- runFunc并发超过阈值:
circuit.circuitError{concurrencyLimitReached: true, msg: "throttling connections to command"} - fallbackFunc并发超过阈值:
circuit.circuitError{circuitOpen: true, msg: "throttling concurrency to fallbacks"}
- runFunc并发超过阈值:
- 当状态为“打开”:
- fallbackFunc 返回的 error
- nil
其中 fallbackFunc 的 error 参数可能为:
- runFunc 返回的 error,除了 circuit.BadRequest
- circuit 返回的
- 当状态为“打开”:
circuit.circuitError{concurrencyLimitReached: true, msg: "circuit is open"} - 当并发请求超过阈值:
- runFunc并发超过阈值:
circuit.circuitError{concurrencyLimitReached: true, msg: "throttling connections to command"}
- runFunc并发超过阈值:
- 当状态为“打开”:
- nil
业务系统中的实际应用
在我的业务系统中,OpenToClosed接口的实现,不打算使用hystrix默认的进入“半打开”的逻辑:定时放行部分调用。因为这样可能会影响到上游的业务请求,并且在fallbackFunc中,我会去调用异地热备服务。所以进入“半打开”状态,我选择自己实现OpenToClosed接口,策略如下:
- 当断路器进入“打开”状态时,启动下游服务健康检查定时器,通过模拟业务请求调用下游服务
- 如果调用成功了,并且累积成功调用次数达到一定阈值,此时
OpenToClosed.Allow(now time.Time) bool根据一定概率返回 true,断路器进入“半打开”状态 - 如果调用失败了,
OpenToClosed.Allow(now time.Time) bool返回 false
- 如果调用成功了,并且累积成功调用次数达到一定阈值,此时
- 当断路器进入“半打开”状态
- 如果调用成功了,进行计数,达到阈值后,断路器进入“关闭”状态,并且停止下游健康检查定时器
- 如果调用失败了,断路器回到“打开”状态
实现代码:
package circuit
import (
"math/rand"
"sync"
"time"
"github.com/cep21/circuit"
"github.com/cep21/circuit/v3/faststats"
)
type ConfigureCloser struct {
CloseOnSuccessfulAttemptsCount int64
ReopenHealthCheck \*HealthCheck
}
type Closer struct {
reopenHealthCheck \*HealthCheck
successfulAttempts faststats.AtomicInt64
closeOnSuccessfulAttemptsCount int64
}
func NewCloser(config ConfigureCloser) circuit.OpenToClosed {
return &Closer{
reopenHealthCheck: config.ReopenHealthCheck,
closeOnSuccessfulAttemptsCount: config.CloseOnSuccessfulAttemptsCount,
}
}
// start health check when circuit is opened
func (c \*Closer) Opened(now time.Time) {
c.reopenHealthCheck.start()
}
// stop health check when circuit is closed
func (c \*Closer) Closed(now time.Time) {
c.reopenHealthCheck.stop()
}
// half-open
func (c \*Closer) Allow(now time.Time) bool {
return c.reopenHealthCheck.ok()
}
func (c \*Closer) Success(now time.Time, duration time.Duration) {
c.successfulAttempts.Add(1)
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrBadRequest(now time.Time, duration time.Duration) {
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrInterrupt(now time.Time, duration time.Duration) {
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrConcurrencyLimitReject(now time.Time) {
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrShortCircuit(now time.Time) {
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrFailure(now time.Time, duration time.Duration) {
c.successfulAttempts.Set(0)
c.reopenHealthCheck.reset()
}
func (c \*Closer) ErrTimeout(now time.Time, duration time.Duration) {
c.successfulAttempts.Set(0)
c.reopenHealthCheck.reset()
}
func (c \*Closer) ShouldClose(now time.Time) bool {
return c.successfulAttempts.Get() \> c.closeOnSuccessfulAttemptsCount
}
type ConfigureHealthCheck struct {
TickDuration time.Duration
Run func() bool
Threshold int64
AllowProbability int
}
type HealthCheck struct {
running bool
stopSignalCh chan struct{}
count faststats.AtomicInt64
mu sync.Mutex
config ConfigureHealthCheck
}
func NewHealthCheck(config ConfigureHealthCheck) \*HealthCheck {
return &HealthCheck{
stopSignalCh: make(chan struct{}),
config: config,
}
}
func (h \*HealthCheck) start() {
h.mu.Lock()
defer h.mu.Unlock()
if h.running {
return
}
h.running = true
h.count.Set(0)
go func() {
tick := time.Tick(h.config.TickDuration)
for {
select {
case \<-tick:
if h.config.Run() {
h.count.Add(1)
} else {
h.count.Set(0)
}
case \<-h.stopSignalCh:
return
}
}
}()
}
func (h \*HealthCheck) stop() {
h.mu.Lock()
defer h.mu.Unlock()
if !h.running {
return
}
h.stopSignalCh \<- struct{}{}
h.running = false
h.count.Set(0)
}
func (h \*HealthCheck) ok() bool {
h.mu.Lock()
defer h.mu.Unlock()
if !h.running {
return true
}
return h.count.Get() \> h.config.Threshold && h.config.AllowProbability \> rand.Intn(101)
}
func (h \*HealthCheck) reset() {
h.count.Set(0)
}